Solenoid valves are control units that can be electrically de-energised or energised to allow the flow of fluids. They have an actuator, which takes the form of electromagnets. If the solenoid valve is energised, the pivoted armature or plunger is against the spring action. But what if it is de-energised? It returns to its original position by the action of the spring. The valves are primarily found in different equipment and plants. You will find several designs that are appropriate for various applications. To know more about the uses and applications, you can read this article further. Before that, you can learn the components and types of solenoid valves.
What are the components of the solenoid valves?
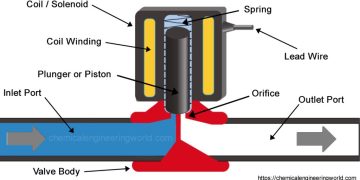
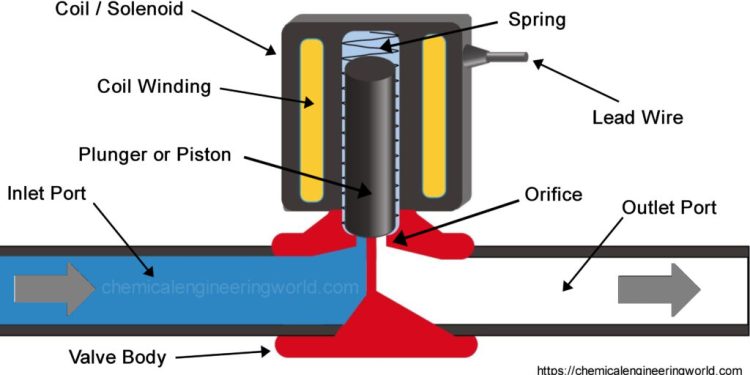
Solenoid valves are separated into the valve body and the solenoid. The solenoid parts depend upon the type of action. The valve body components are like any other valve, but their designs and materials vary. Here are a few of the features given below.
- Coil: The solenoid valve has a prime part called a coil that comprises an insulated copper wire. This wire is firmly wound around the tube. Then, an electric current is applied after generating the magnetic field.
- Diaphragm: One of the flexible materials is the diaphragm. It isolates the assembly of solenoids from the liquid or fluid. It is designed to contain fluid pressure.
- Seal: The seal is similar to the diaphragm as it can isolate solenoid assembly. Additionally, it can separate the external environment. You can attain different seal materials depending upon the process fluid and application. Some of them include EPDM, NBR, PTFE, and FKM.
- Bonnet: The top of the valve body consists of the bonnet. The stem and core tube enter the valve by extending through the valve bonnet.
- Fixed core: To improve magnetic flux, a fixed centre is installed at the end of the tube.
What are the types of solenoid valves?
Before choosing a solenoid valve, you must consider the fluid type, materials and other specifications. Additionally, you must know the various styles. So, read on and learn about them.
- Pilot-operated valves: The solenoid activates a small valve, and a large valve is opened at high pressure. It allows the release of air, gas and steam in large quantities.
- Direct-acting valves: This valve doesn’t depend upon outside pressure to open magnetically. In the direct-acting valve, a coil is used to open by lifting the seal and shaft.
- Two-way valves: The most common valve with two ports closes or permits the flow alternatively. The operation of the valve is specified as “normally closed” or “normally open.” The “normally closed” valve will stay closed as long as you open the power source, whereas the “normally open” valve will stay open if the current is applied.
- Four-way valves: As the name suggests, they have four-port connections and are utilised with an actuator. They are specified to be normally open, universal or normally closed.
What are the typical applications of solenoid valves?
Since fluid flow can be controlled with ease, it is used in places of automation like factories or robotics. The solenoid valves are also used in different industrial and manufacturing plants. You will find the valves in ventilator systems, dialysis machines, etc. The food and pharmaceutical industries use them so that they can comply with their hygienic needs.
Solenoid valves are compatible with AC and DC voltage and can be installed vertically or horizontally. One of the significant advantages is that they consume less power. You can ensure that they provide you with safe switching, considerable service life and a high level of reliability.